In this procedure, we create a Python script that connects to a large language model (LLM) to facilitate the creation of Ansible playbooks using natural language queries. We begin by creating the Ansible deployment environment on a staging server, with a hosts file and inventory.ini file that correspond to a group of servers. We enable passwordless entry from the staging server to the servers, and ensure that visudo is configured for passwordless escalation to root using sudo.
The system does not run the generated playbook; the human operator must review it and then execute it manually.
A preview of the system in operation
To use the system, an operator starts the playbook generator at the command line:
python3 playbook_generator.py
The operator enters a natural language query, such as:
CLI> install net-tools on node03
The system generates a playbook:
📌 Saving Playbook: playbook_20250320123755.yml
✅ Playbook saved: playbook_20250320123755.yml
CLI> quit
The operator runs the playbook:
(llmansible_env) root@node01:/opt/llmansible# ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/playbook_20250320123755.yml
PLAY [Install net-tools on node03] ***
TASK [Gathering Facts] *
ok: [node03]
TASK [Install net-tools] *
changed: [node03]
PLAY RECAP *
node03 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Escalating to root using sudo su
Enter the following command:
sudo su
Configuring the staging server
On the staging server, enter the following commands:
apt clean && update && sudo apt upgrade -y<br>reboot
Enter the following commands:
sudo su
apt install -y ansible python3-pip tmux python3-venv \
openssh-client pkg-config
cd /etc
notepad hosts
Use the nano editor to add the following text to the file. Modify IP address values as appropriate for your setup:
127.0.1.1 node01
192.168.56.82 node02
192.168.56.83 node03
192.168.56.84 node04
192.168.56.85 node05
Save and exit the file.
Preparing the nodes for automation
On each node, ensure that the server has a host name, static IP address, and has visudo configured for passwordless escalation to root with sudo su.
For each node:
Enter the following commands:
sudo su
visudo
Use the nano editor to add the following text to the bottom of the file (substitute your login name):
desktop ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
Save and exit the file.
Generating SSH keys
On the staging server, enter the following commands:
sudo su
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -N ""
Copying the public SSH key to all nodes
Enter the following commands (substitute login username and server name as appropriate for your installation.
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub desktop@node02
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub desktop@node03
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub desktop@node04
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub desktop@node05
Verifying that passwordless login via SSH is working
Enter the following commands (modify login user name and host name as appropriate to match your installation):
ssh desktop@node02
exit
Creating the inventory.ini file
Enter the following commands:
cd /opt
mkdir llmansible
cd llmansible
nano inventory.ini
Use the nano editor to add the following text to the file:
[all]
node02 ansible_host=192.168.56.82 ansible_user=desktop
node03 ansible_host=192.168.56.83 ansible_user=desktop
node04 ansible_host=192.168.56.84 ansible_user=desktop
node05 ansible_host=192.168.56.85 ansible_user=desktop
[all:vars]
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.ssh/id_rsa
ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
Save and exit the file.
Creating the config.ini file
Enter the following command:
nano config.ini
Use the nano editor to add the following text to the file (modify values as appropriate to match your installation):
[LLM]
system_prompt = You are an AI that generates structured Ansible playbooks. Ensure: The playbook is idempotent. It installs required packages using apt (for Ubuntu) or yum (for CentOS). It does not execute shell commands directly. It follows proper YAML formatting. assume that OS is ubuntu unless otherwise stated. only respond with the contents of the ansible playbook, nothing more. do not offer multiple playbooks. do not add commentary.
api_url = https://api.lemonfox.ai/v1/chat/completions
api_token = your-api-token
model_name = llama-8b-chat
Save and exit the file.
Creating a Python virtual environment (venv), and adding Python dependencies
Enter the following commands:
cd /opt/llmansible
python3 -m venv llmansible_env
source llmansible_env/bin/activate
Adding Python dependencies using pip
Enter the following command:
pip install PyYAML requests
Creating the playbook_generator.py file
Enter the following command:
nano playbook_generator.py
Use the nano editor to add the following text to the file:
# MIT license Gordon Buchan 2025
# see https://opensource.org/license/mit
# some of the code was generated with the assistance of AI tools.
import requests
import configparser
import os
import re
import yaml
from datetime import datetime
# Load Configuration
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read("config.ini")
LLM_API_URL = config.get("LLM", "api_url")
LLM_API_TOKEN = config.get("LLM", "api_token")
LLM_MODEL = config.get("LLM", "model_name")
SYSTEM_PROMPT = config.get("LLM", "system_prompt")
PLAYBOOK_DIR = "/opt/llmansible/playbooks"
def extract_yaml(text):
"""Extracts valid YAML content and removes explanations or malformed sections."""
# Remove Markdown-style code block markers (e.g., ```yaml)
text = re.sub(r"```(yaml|yml)?", "", text, flags=re.IGNORECASE).strip()
# Capture the first YAML block (ensuring it's well-formed)
match = re.search(r"(?s)(---\n.+?)(?=\n\S|\Z)", text)
if match:
yaml_content = match.group(1).strip()
# Remove trailing incomplete YAML lines or explanations
yaml_content = re.sub(r"\n\w+:\s*\"?[^\n]*$", "", yaml_content).strip()
# Validate extracted YAML before returning
try:
yaml.safe_load(yaml_content) # If this fails, the YAML is invalid
return yaml_content
except yaml.YAMLError as e:
print(f"❌ YAML Validation Error: {e}")
return ""
print("❌ Error: No valid YAML found.")
return ""
def query_llm(prompt):
"""Queries the LLM API and extracts a valid Ansible playbook."""
payload = {
"model": LLM_MODEL,
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
],
"max_tokens": 2048
}
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {LLM_API_TOKEN}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.post(LLM_API_URL, json=payload, headers=headers)
print("\n🔍 API RAW RESPONSE:\n", response.text)
try:
response_json = response.json()
llm_response = response_json["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
yaml_content = extract_yaml(llm_response)
if not yaml_content:
print("❌ Error: No valid YAML extracted.")
return ""
print("\n✅ Extracted YAML Playbook:\n", yaml_content)
return yaml_content
except (KeyError, IndexError):
print("❌ Error: Unexpected API response format.")
return ""
def save_playbook(machine, command, playbook_content):
"""Saves the extracted YAML playbook if it's valid."""
if not playbook_content.strip().startswith("---"):
print("❌ Error: Extracted content is not a valid Ansible playbook. Skipping save.")
return None
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
playbook_name = f"playbook_{timestamp}.yml"
playbook_path = os.path.join(PLAYBOOK_DIR, playbook_name)
os.makedirs(PLAYBOOK_DIR, exist_ok=True)
print(f"\n📌 Saving Playbook: {playbook_name}")
with open(playbook_path, "w") as f:
f.write(playbook_content)
return playbook_name
def main():
"""CLI Operator Console."""
while True:
user_input = input("CLI> ")
if user_input.lower() in ["exit", "quit"]:
break
llm_response = query_llm(user_input)
if llm_response:
playbook_name = save_playbook("all", user_input, llm_response)
if playbook_name:
print(f"✅ Playbook saved: {playbook_name}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Save and exit the file.
Creating an Ansible playbook using the playbook generator
Ensuring that you are in the Python venv
Ensure that you are already in the Python venv. If not, enter the following commands:
cd /opt/llmansible
source llmansible_env/bin/activate
Enter the following command:
python3 playbook_generator.py
The operator enters a natural language query, such as:
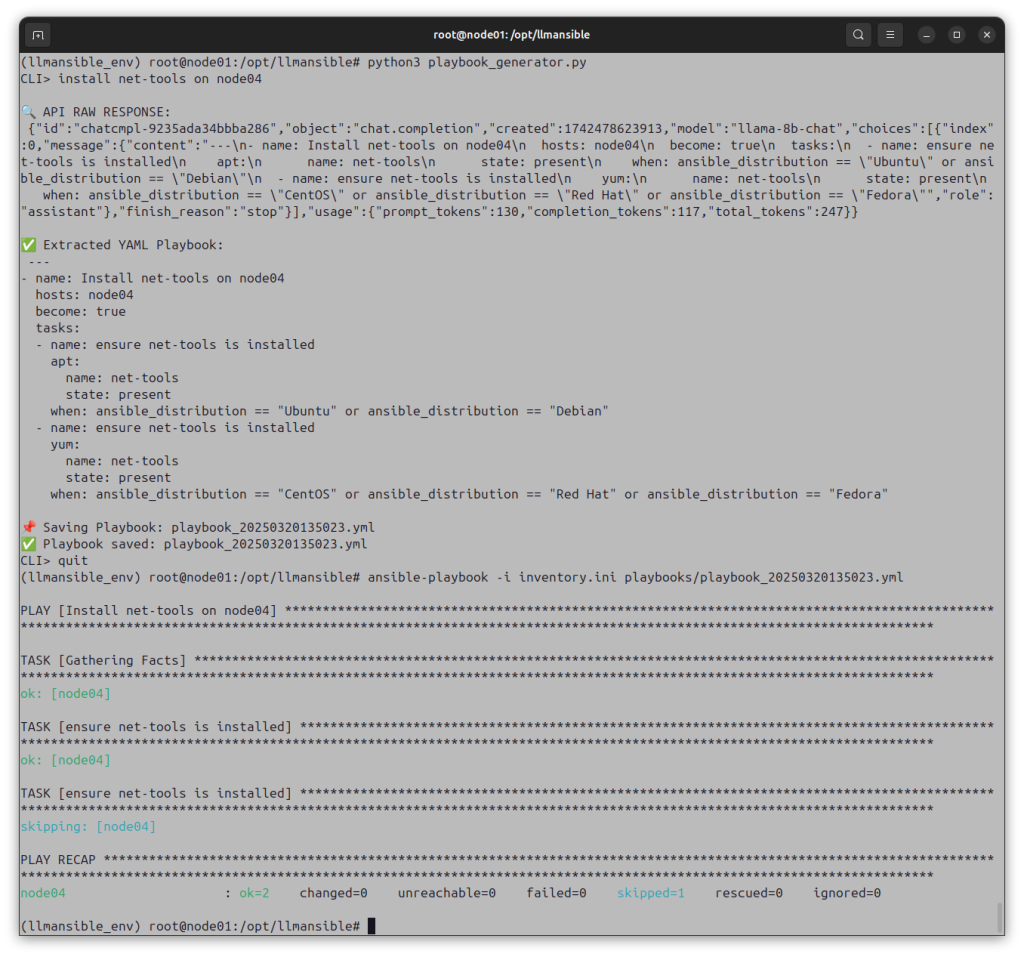
CLI> install net-tools on node04
🔍 API RAW RESPONSE:
{"id":"chatcmpl-923543777fb7a294","object":"chat.completion","created":1742474275313,"model":"llama-8b-chat","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"content":"---\n- name: Install net-tools on node04\n hosts: node04\n become: yes\n tasks:\n - name: Install net-tools\n apt:\n name: net-tools\n state: present","role":"assistant"},"finish_reason":"stop"}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":130,"completion_tokens":47,"total_tokens":177}}
✅ Extracted YAML Playbook:
name: Install net-tools on node04
hosts: node04
become: yes
tasks:
name: Install net-tools
apt:
name: net-tools
state: present
📌 Saving Playbook: playbook_20250320135023.yml
✅ Playbook saved: playbook_20250320135023.yml
CLI> quit
The operator runs the playbook:
(llmansible_env) root@node01:/opt/llmansible# ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/playbook_20250320135023.yml
PLAY [Install net-tools on node04] ***
TASK [Gathering Facts] *
ok: [node04]
TASK [Install net-tools] *
changed: [node04]
PLAY RECAP *
node04 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0